Impact of Passing Through Negotiated Rebates for Oral Antidiabetic Drugs (OADs) on Medical Spending
-
The total economic cost of diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus in the US reached $327 billion in 2017—$237 billion in direct medical costs and $90 billion in reduced productivity
-
High out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for diabetes medicines are key barriers to taking prescribed medicines that can reduce risk of diabetes complications, hospitalization and emergency visits, and associated healthcare costs
-
GlobalData estimates that sharing manufacturer rebates for brand OADs directly with commercially insured patients can reduce their net drug out-of-pocket spending
Impact of Passing Through Negotiated Rebates for Oral Antidiabetic Drugs (OADs) on Medical Spending
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 13% of all the US adults have diabetes, and even more meet criteria for prediabetes. Aside from its pervasive nature, it is known that diabetes presents a substantial health and economic burden that disproportionately affects Black, Native American/Alaskan Native, and Hispanic populations. A study commissioned by the American Diabetes Association reports that diagnosed diabetes cost the nation $327 billion in 2017, including $237 billion in direct medical costs and $90 billion in reduced productivity. The study also noted that there are differences in diabetes-related health expenditures across race and ethnicity groups; for example, Black patients with diabetes incur 7% higher diabetes-attributed healthcare expenditures on average compared to white patients. Disparities in diabetes outcomes arise, in great part, from the inequities in the healthcare system, which can be exemplified and exacerbated through inequitable access to essential diabetes medications. Extensive evidence links better medicine adherence to reduced diabetes complications, lower medical spending, and lower mortality.
Despite the known benefits of taking medication as prescribed, poor medication adherence among DM patients is a significant challenge. One study estimated that only about 59% of commercially insured adults with diagnosed, medication-treated Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus have their blood glucose level under control, and that lack of control was associated with $6,680 in higher annual healthcare expenditures. Research shows that high OOP costs are strongly associated with lower drug adherence. This issue is even more pronounced in Black and Hispanic populations, who are more likely to report cost-related nonadherence than white populations. Lowering financial barriers to prescription drugs could improve medicine adherence for all patients and has the potential to reduce disparities in chronic disease management, particularly by improving access to medicines for populations most sensitive to financial barriers.
The average total annual drug and medical spending per commercially insured beneficiary, High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) combined, with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) treated with brand OADs was $20,783 in 2018, of which patients paid $4,267 OOP. Although improved adherence increases spending on diabetes medicines, improved adherence is associated with decreased spending on avoidable care for diabetes-related complications. One study estimates that improved adherence to diabetes medications could avert nearly 700,000 emergency department visits and 341,000 hospitalizations—an annual savings of $4.7 billion. Using estimates derived from the literature on the association between adherence and medical spending, Globaldata estimates that adherence improvements due to passing through negotiated rebates for OADs at the pharmacy could decrease total annual drug and medical spending per capita by 4.9% among commercially insured patients who use brand OADs, inclusive of plan and patient OOP spending as well as increased OAD spending associated with improved adherence. This finding is consistent with literature showing that the medical savings generated from better adherence offset the increased drug spending for patients with T2DM. The medical cost savings are likely to be mostly driven by the reduction in hospitalizations and emergency visits due to better adherence to diabetic medicines and therefore presumably better diabetes care management.
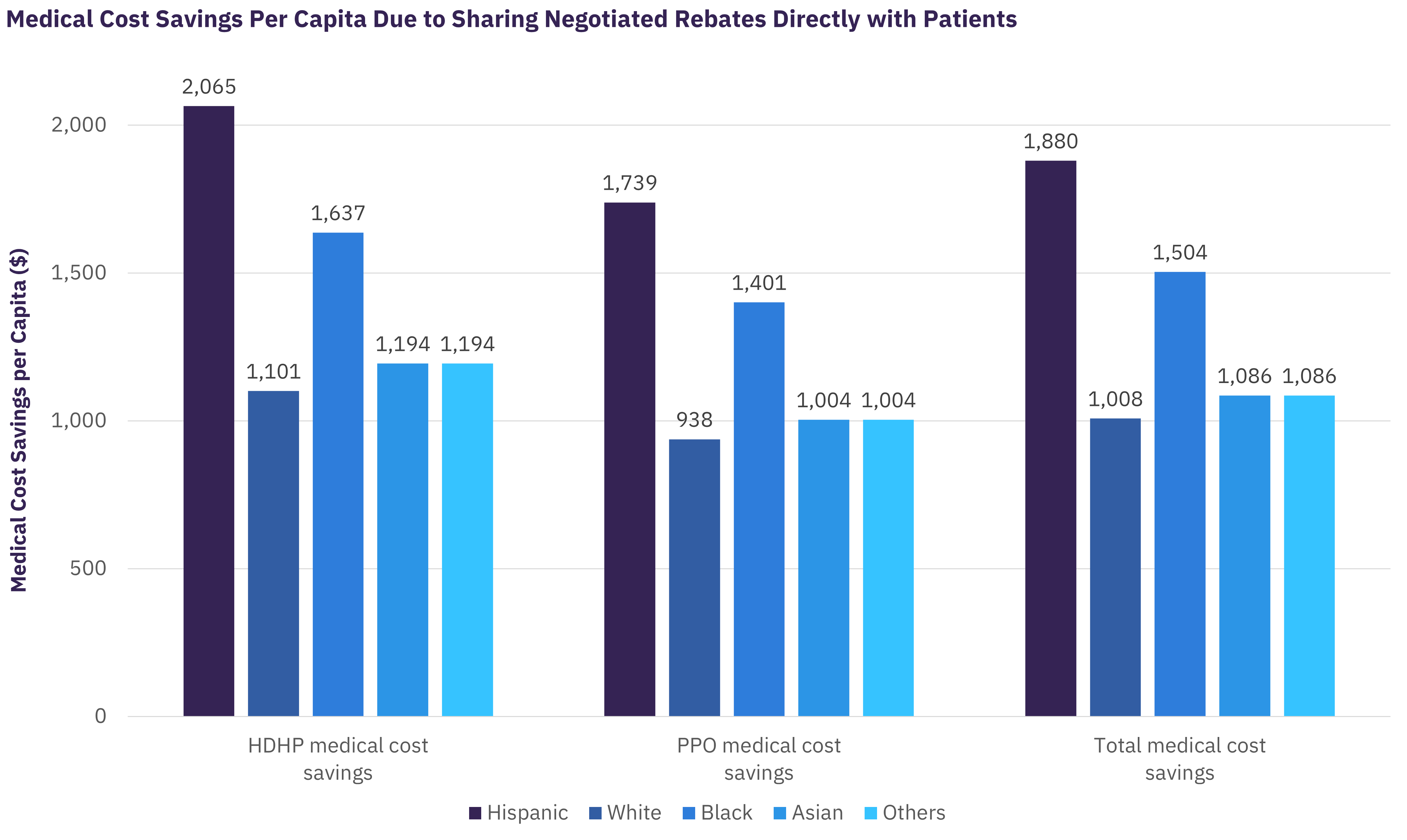
The estimated effects differ by beneficiary race and ethnicity. Among commercially insured Hispanic patients, for example, GlobalData’s report on “The Impact of Sharing Manufacturer Rebates for Oral Anti-Diabetic Medications at the Point of Sale with Patients in the Commercial Market” estimates that passing through negotiated rebates at the pharmacy would lead to 9% lower total medical and drug spending, or more than twice the 4.2% savings experienced by white patients.
To highlight the extent to which the reductions in total spending associated with rebate pass-through are driven by reduced medical spending, GlobalData presents its findings in the following report. For example, for Hispanic patients, rebate sharing would lead to a 15.8% increase in the number of OAD fills annually within the deductible and cost sharing phases, thereby increasing total net OAD spending by 11.7%. However, per capita savings from improved medicine adherence would decrease total annual medical costs by 11.0%, which altogether lead to a 9.0% reduction in total annual drug and medical costs due to rebate sharing.
The larger relative reduction in medical cost among some minority groups further exemplifies how passing through rebates at the pharmacy could not only reduce the overall medical expenditures but could also potentially reduce the level of racial disparities in chronic disease management attributed to the financial barriers in procuring prescription drugs.
Related Data & Insights
Related Companies
United States of America
United States of America
China
Switzerland
United States of America
United States of America
United States of America
United States of America
Germany
France
Don’t wait - discover a universe of connected data & insights with your next search. Browse over 28M data points across 22 industries.
Access more premium companies when you subscribe to Explorer
Get in touch about GlobalData Company reports
Contact the team or request a demo to find out how our data can drive your business forward