US Federal Reserve Hikes Interest Rates to Curb Inflation
-
The US Federal Reserve has hiked interest rates for the first time since December 2018
-
The inflation rate in the US touched 7.9% in February 2022
-
The hike in interest rate will affect the loan and mortgage sector
US Federal Reserve Hikes Interest Rates to Curb Inflation
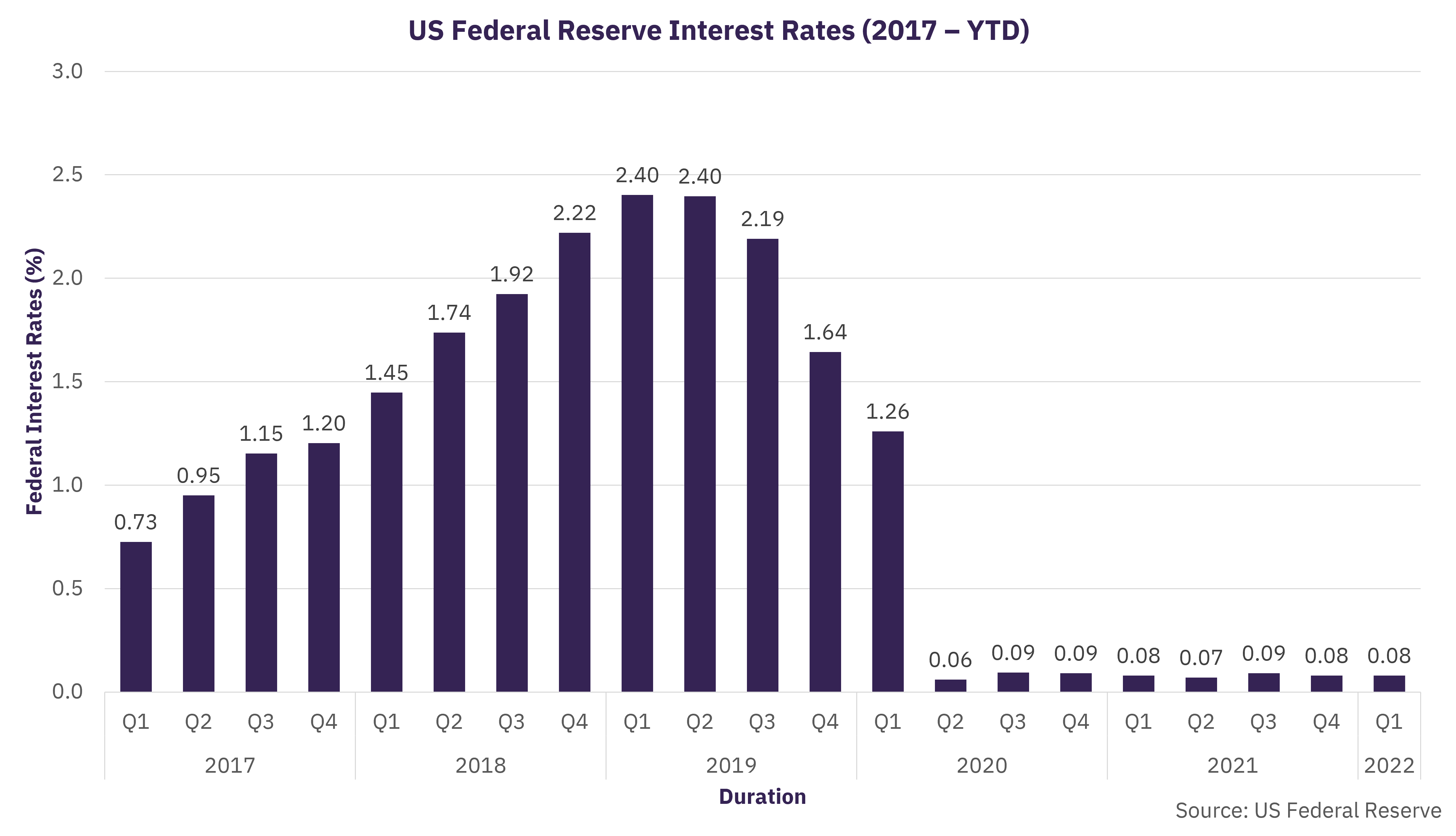
The US Federal Reserve, on March 16, 2022, announced that the interest rates set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) would increase for the first time since December 2018. The interest rates, also called the Effective federal funds rate (EFFR), would be raised from near-zero to 0.25-0.5%. It also plans six more increases by the end of the year to lift the effective rate to nearly 2% by early 2023 to curb the inflation rate, which is at a 40-year high.
Why the hike in the interest rate?
The increase in interest rate is a result of concerns over rising inflation. The central bank pulled the federal interest rates to near-zero following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. The lower federal interest rates allowed banks to borrow and lend their excess reserves at lower rates overnight, ensuring that the public and businesses borrow money at lower interest rates. Such lower borrowing costs supported the sliding economy during the pandemic, which provided a wealth surplus and a spending boom. This led to supply shortages and the phenomenon of inflation on a roll. Many jobs were created in recent months, resulting in a decline in unemployment rates in almost all states. The supply-demand imbalance and unemployment rate coupled with the ongoing sanctions on Russia led to additional upward pressure on inflation. Therefore, the federal interest rates were hiked assessing the situation and ensuring that the inflation rate is clamped down to 2% in the next year.
What is at stake for the public?
The federal interest rate is a benchmark interbank borrowing interest rate. The consumers or borrowers will eventually bear the effects of the increase in interest rate. Since the pandemic, the interest rate has been constant at 0.08%, but the recent hike will ensure an increase in borrowing costs. Additional increase in federal rates will compound the effect of rising interest rates and limit borrowing. The payment of loans, mortgages, and credit cards are some areas that will witness the immediate heat of the hike in rates.
The supply-demand misbalance has caused an increase in the price indices for gasoline, shelter, and food, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, which pushed inflation to nearly 7.9% in February 2022. Thus, increasing the federal interest rate will ensure a slower pace of borrowing and restrain spending. The reaction of the market, borrowers, and consumers to the hike in interest rates remains to be seen.
Related Data & Insights
Don’t wait - discover a universe of connected data & insights with your next search. Browse over 28M data points across 22 industries.
Access more premium companies when you subscribe to Explorer